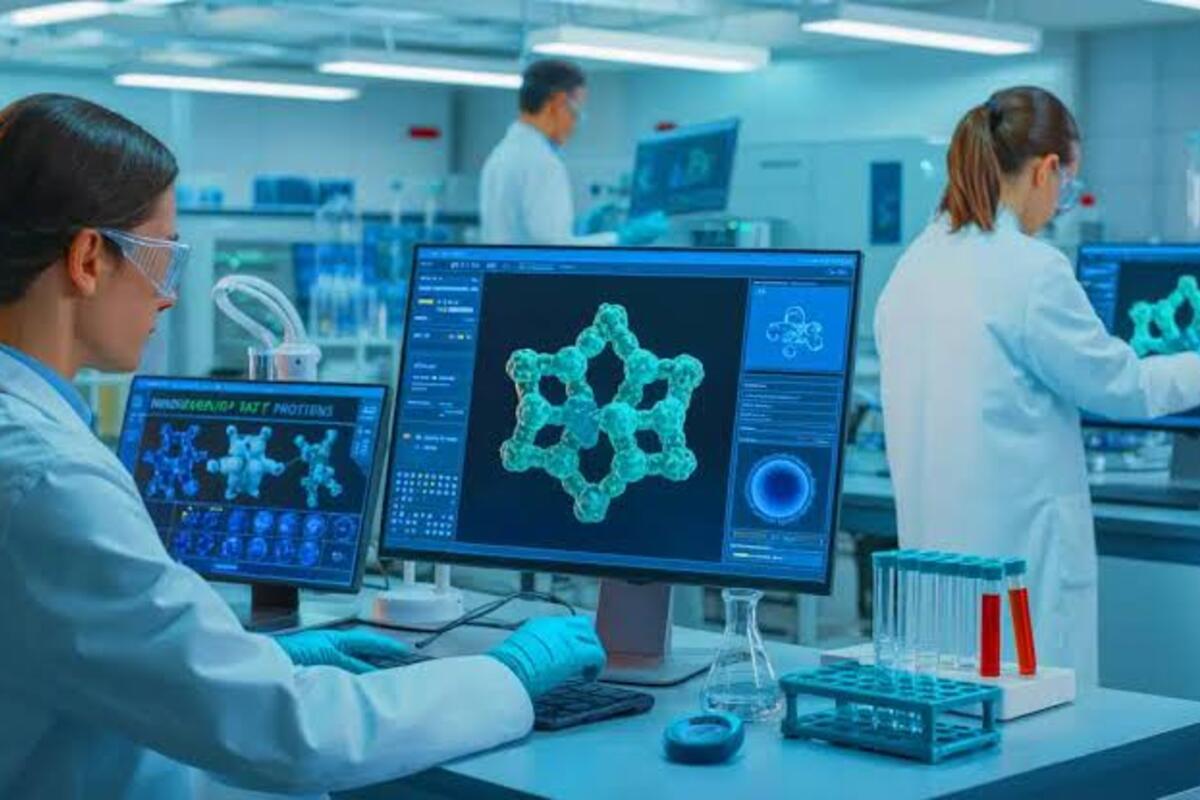
A groundbreaking advancement in cancer therapy has emerged with the development of synthetic proteins engineered by artificial intelligence (AI). These AI-designed proteins, known as minibinders, are revolutionizing cancer treatment by enabling the immune system to target and destroy tumor cells with unprecedented precision and speed.

Traditionally, cancer therapies such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy have been time-consuming and often come with significant side effects. The process of developing effective treatments can span several years, involving extensive research and clinical trials. However, AI is now accelerating this timeline dramatically. Researchers have utilized AI to design minibinder proteins that can specifically bind to cancer cell markers, effectively guiding the body’s immune cells to recognize and eliminate these malignant.
The design process involves training AI models to understand the complex structures of proteins and their interactions with various molecules. Once trained, these models can generate novel protein sequences that are optimized to bind to specific targets on cancer cells. This approach not only speeds up the development of cancer therapies but also enhances their specificity, reducing the likelihood of damage to healthy cells.
One of the most significant advantages of AI-designed minibinders is their ability to be tailored to individual patients. By analyzing the unique characteristics of a patient’s cancer cells, AI can create personalized treatments that are more effective and have fewer side effects compared to traditional therapies.
This innovation marks a pivotal moment in the field of oncology, offering hope for more effective and personalized cancer treatments. As AI continues to advance, its integration into medical research promises to further transform the landscape of cancer care, potentially leading to faster, safer, and more targeted therapies for patients worldwide.